An Overview of Lymphoma
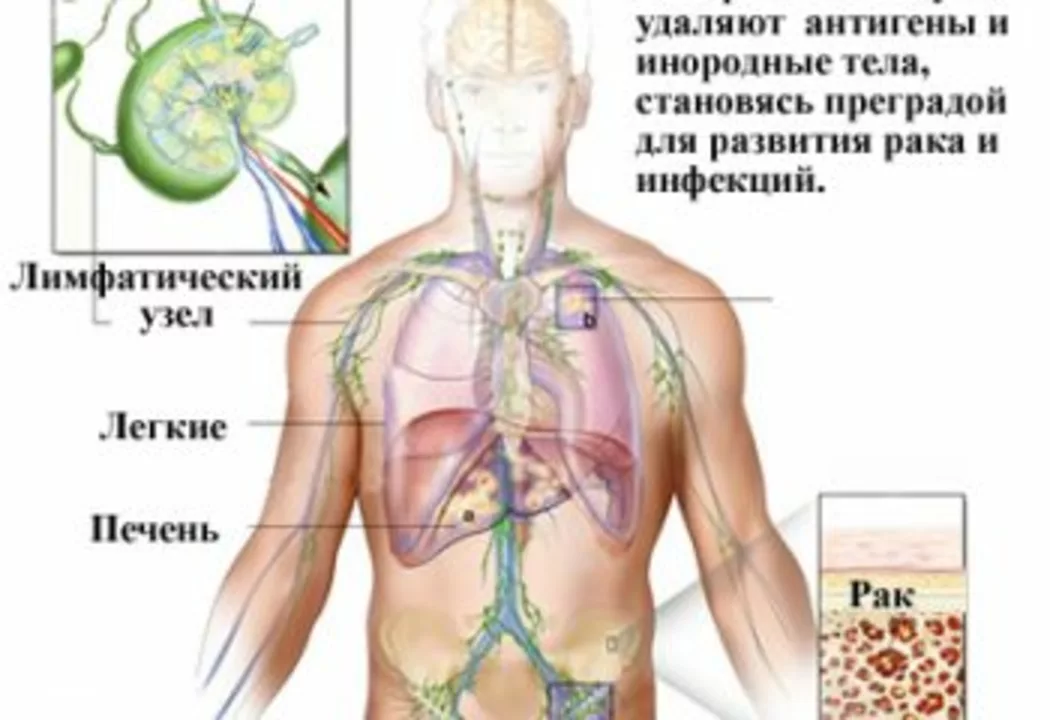
Before diving into the details of lymphoma, it's essential to have a basic understanding of what this cancer is all about. Lymphoma is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, which is responsible for fighting infections and maintaining the balance of body fluids. The lymphatic system consists of lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoma can be categorized into two main types: Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. In this article, I will discuss the different types, symptoms, and causes of lymphoma, in the hope of helping you gain a better understanding of this disease.
Types of Lymphoma: Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Hodgkin's lymphoma, also known as Hodgkin's disease, is a type of lymphoma that is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells. These cells are abnormal, large, and multinucleated cells that can be identified under a microscope. Hodgkin's lymphoma is relatively rare, accounting for about 10% of all lymphoma cases. This cancer usually starts in the lymph nodes in the neck or chest and can spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. Hodgkin's lymphoma is typically diagnosed in young adults and people over the age of 50. With the right treatment, Hodgkin's lymphoma has a high cure rate.
Types of Lymphoma: Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) is a more common type of lymphoma, accounting for about 90% of all lymphoma cases. Unlike Hodgkin's lymphoma, NHL does not have the characteristic Reed-Sternberg cells. There are several subtypes of NHL, which can be classified as either aggressive (fast-growing) or indolent (slow-growing). Some common subtypes of NHL include diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma. NHL can affect people of all ages, but the risk increases as you get older. The treatment for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma depends on the type, stage, and other factors, but may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Lymphoma
One of the earliest and most common symptoms of lymphoma is painless swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, armpit, or groin. This swelling may occur suddenly or gradually over time. Other symptoms of lymphoma can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease, but may include:
- Fever
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night sweats
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Itching
- Cough
It is essential to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other, less serious conditions. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult your doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
Causes of Lymphoma: Genetic Factors
Although the exact cause of lymphoma is unknown, several factors are known to increase the risk of developing this cancer. One such factor is genetic predisposition. Some people inherit genes that make them more susceptible to developing lymphoma. For example, having a family history of lymphoma or other types of cancer can increase your risk. Additionally, certain genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome or Klinefelter syndrome, can also increase the likelihood of developing lymphoma.
Causes of Lymphoma: Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain environmental factors can also increase the risk of developing lymphoma. These factors include:
- Exposure to radiation or certain chemicals, such as pesticides, solvents, or hair dyes
- Working in occupations that involve exposure to certain chemicals, such as farming, rubber manufacturing, or painting
- Taking certain medications, such as immunosuppressive drugs or chemotherapy
Although these factors can increase the risk of lymphoma, it is important to remember that not everyone who is exposed to these factors will develop the disease.
Causes of Lymphoma: Viral and Bacterial Infections
Some viral and bacterial infections are also known to increase the risk of developing lymphoma. For example, the Epstein-Barr virus, which causes mononucleosis, has been linked to an increased risk of Hodgkin's lymphoma and certain types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Other infections that can increase the risk of lymphoma include human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus (HTLV-1), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and Helicobacter pylori bacteria.
Preventing and Detecting Lymphoma
While it may not be possible to prevent lymphoma entirely, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. For example, you can:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoid exposure to harmful chemicals and radiation
- Practice safe sex and avoid sharing needles to reduce the risk of viral infections
Early detection of lymphoma is crucial for successful treatment. If you notice any symptoms of lymphoma, such as swollen lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, or night sweats, it is essential to consult your doctor promptly for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.

Michelle Guatato
May 5, 2023 AT 22:56The pharmaceutical industry has long been interested in keeping the public dependent on costly treatments, and that agenda subtly shapes how medical information is presented. When you read about lymphoma, notice how the language often emphasizes the inevitability of chemotherapy while downplaying natural immune strategies. The subtle framing pushes patients toward expensive drug regimens that boost corporate profits. Behind the scenes, lobbying groups fund research that steers focus toward patented therapies rather than lifestyle prevention. This isn’t just about science; it’s about control and cash flow. Keep a skeptical eye on the sources that dictate the narrative, because the same entities that profit from treatments also influence what we learn about causes and prevention.
Gabrielle Vézina
May 6, 2023 AT 00:16Lymphoma symptoms are often blown out of proportion by mainstream health media and the panic you see is just a manufactured hype. The facts are simple they are just swollen nodes and occasional night sweats it’s not a headline crisis. Doctors love to over‑diagnose because it fills their appointment books and boosts insurance claims. While the article lists every possible cause you can’t ignore the fact that most people never develop it despite exposure to the same chemicals. So the real story is that fear sells more than prevention.
carl wadsworth
May 6, 2023 AT 01:40Understanding lymphoma starts with recognizing that the lymphatic system is a critical component of our immune defense, and any disruption can have far‑reaching consequences. First, the distinction between Hodgkin’s and non‑Hodgkin’s types is not just academic; it determines treatment pathways and prognosis, so patients should be empowered to ask their clinicians about specific subtypes. Second, early symptoms such as painless lymph node swelling are often dismissed as minor infections, yet they deserve prompt medical evaluation to rule out malignancy. Third, lifestyle factors-balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management-play a supportive role in maintaining robust immune surveillance. Fourth, while genetics can predispose individuals, most cases arise without a clear hereditary link, underscoring the importance of environmental awareness. Fifth, exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, and occupational hazards has been epidemiologically linked to higher lymphoma rates, so minimizing contact whenever possible is prudent. Sixth, viral agents like Epstein‑Barr virus and HIV are well‑documented contributors, highlighting the value of vaccination and safe practices. Seventh, early detection through routine physical exams and imaging when indicated can dramatically improve outcomes, so staying vigilant is key. Eighth, contemporary therapies have advanced beyond traditional chemotherapy, incorporating targeted agents and immunotherapies that can offer better tolerability and response rates. Ninth, multidisciplinary care involving hematologists, oncologists, radiologists, and supportive specialists ensures a comprehensive approach. Tenth, patients should be proactive in discussing clinical trial options, as research continues to refine treatment algorithms. Eleventh, psychosocial support is vital; dealing with a cancer diagnosis can be emotionally taxing, and resources like counseling and peer groups make a real difference. Twelfth, survivorship care plans that monitor for late effects of treatment help maintain long‑term health. Thirteenth, family members may benefit from genetic counseling if there’s a strong cancer history. Fourteenth, staying informed through reputable sources empowers patients to make evidence‑based decisions. Fifteenth, never underestimate the importance of a strong support network, whether friends, family, or online communities, as they can provide encouragement through the toughest moments. Finally, remember that each lymphoma journey is unique, and personalized care plans are the cornerstone of effective management.
Neeraj Agarwal
May 6, 2023 AT 04:26It is essential to keep the grammar correct when discussing medical topics because precision matters. The article mentions "exposure to radiation or certain chemicals" and that phrasing is accurate, however, the phrase "certain chemicals" could be clarified with examples such as pesticides or solvents. Also, the sentence "Some viral and bacterial infections are also known to increase the risk" should use "viral" and "bacterial" as adjectives consistently. A minor typo in "immunosupressive" should be corrected to "immunosuppressive". Overall, the content is solid; just watch for these small edits to maintain credibility.
Rose K. Young
May 6, 2023 AT 07:13Honestly, this reads like a textbook for people who already know everything.
Christy Pogue
May 6, 2023 AT 10:00Great job breaking down a complex disease into easy‑to‑understand sections! I love how the article highlights both lifestyle tips and medical advances. It really empowers readers to take charge of their health. Keep sharing these clear, uplifting explanations-we need more positivity in medical writing. Looking forward to more posts like this!
Helena Pearson
May 6, 2023 AT 12:46Reading about lymphoma can feel like navigating a maze, but the way this piece maps out the terrain is refreshing 🌟. The distinction between aggressive and indolent forms is especially crucial for patients making treatment decisions. I appreciate the nod to both cutting‑edge immunotherapy and the timeless wisdom of a healthy lifestyle 🍎. When the article mentions viral triggers, it subtly reminds us that prevention can be as simple as safe practices and vaccination 🛡️. Overall, the blend of science and compassion creates a tapestry that resonates deeply.
Patricia Fallbeck
May 6, 2023 AT 15:33While the article does a competent job of cataloguing symptoms, it fails to capture the existential dread that a lymphoma diagnosis can invoke. One could argue that mere lists of risk factors are insufficient; the human experience demands a more poetic, perhaps tragic, framing. Moreover, the clinical tone strips away the dramatic narrative that would otherwise engage a discerning reader. In short, the piece is informative but lacks the gravitas it so desperately needs.
Brett Snyder
May 6, 2023 AT 18:20We must remember that lymphoma, like many diseases, is more prevalent in our own nation due to lifestyle choices that differ from foreign cultures. The rising rates here reflect a disregard for traditional diets and a reliance on processed foods. This is a clear sign that we need to return to our roots and prioritize home‑grown nutrition. Only then can we hope to curb the incidence that plagues our communities.
Nidhi Jaiswal
May 6, 2023 AT 21:06Lymphoma symptoms are not just random they follow a pattern you can watch for early detection. Unexplained weight loss and night sweats are red flags you should not ignore. If you see swollen nodes get checked quickly. Early treatment improves chances of cure. Simple steps can save lives.
Sunil Sharma
May 6, 2023 AT 23:53Hey, I get where Rose is coming from, but let’s keep it constructive. Everyone’s journey with lymphoma is personal, and sharing solid info helps more than tearing it down. If you’ve got questions about how lifestyle tweaks can complement treatment, I’m happy to chat. The community thrives when we lift each other up. Together we can spread awareness and support.